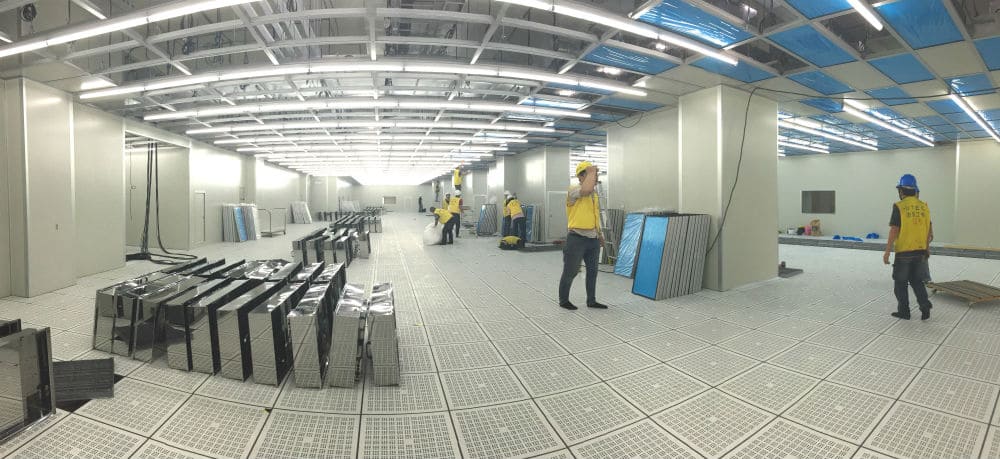
Cleanroom
A cleanroom (or clean room, usually abbreviated to C/R) is an enclosed room that has equipment which controls the amount of particulate matter in the air by using air pressure and filters. It is a facility ordinarily utilized as a part of specialized industrial production or scientific research, including the manufacture of pharmaceutical items and microprocessors.
- Definition
- A manufacturing room with an extremely low level of particles.
- Particles
- Dust, airborne organisms, or vaporized particles.
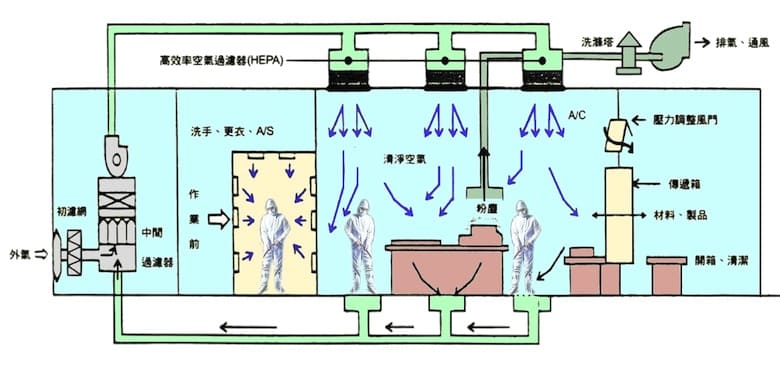
Basic Design Principles
- Prevention of dust accumulation
- Prevention of dust occurrence
- Exclusion of dust
- Prevention of carrying dust into room
- Dehumidification of A/C
- Controlled temperature, humidity and room barometric pressure
Other Design Considerations
- Removal of harmful vapors
- Reduction static electricity
- Prevention of electromagnetic interference
- Air tightness of structures
- Power Spare Solution
- Convenience of management and expandability
- Budget
Cleanroom Classifications
Cleanrooms are classified by how clean the air is. To say more precisely, they are classified according to the number and size of particles permitted per volume of air. Depending on what industry your company is in, and what product being manufactured, the cleanroom will have to comply with certain standards.
ISO 14644-1 & US FED S209E
Both ISO 14644-1 and US FED S209E classifications are most widely used standards. ISO 14644-1 are non-governmental standards developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and US FED-STD-209E is a United States federal standard.
| Class | Maximum Particles | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 µm | 0.2 µm | 0.3 µm | 0.5 µm | 1 µm | 5 µm | ||||||||
| US F. S209E | ISO 14644-1 | (m³) | (ft³) | (m³) | (ft³) | (m³) | (ft³) | (m³) | (ft³) | (m³) | (ft³) | (m³) | (ft³) |
| ISO 1 | 10 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||
| ISO 2 | 100 | 24 | 10 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |||||||
| C-1 | ISO 3 | 1,000 | 35 | 237 | 8 | 102 | 3 | 35 | 1 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| C-10 | ISO 4 | 10,000 | 350 | 2,370 | 75 | 1,020 | 30 | 352 | 10 | 83 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| C-100 | ISO 5 | 100,000 | 3,500 | 23,700 | 750 | 10,200 | 300 | 3,520 | 100 | 832 | 24 | 29 | 0 |
| C-1K | ISO 6 | 1,000,000 | 35,000 | 237,000 | 7,500 | 102,000 | 3,000 | 35,200 | 1,000 | 8,320 | 236 | 293 | 7 |
| C-10K | ISO 7 | * | * | * | * | * | * | 352,000 | 10,000 | 83,200 | 2,360 | 2,930 | 70 |
| C-100K | ISO 8 | * | * | * | * | * | * | 3,520,000 | 100,000 | 832,000 | 23,600 | 29,300 | 700 |
PIC/S and EU GMP Guides
PIC/S GMP (Pharmaceutical Inspection Convention and Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-operation Scheme), also the GMP EU classifications, are more stringent than others, requiring cleanrooms to meet particle counts at operation and at rest. Because it also applies the recommended tolerance for microbes, these classifications are widely used in pharmaceutical-related industries.
| Grade | Maximum Particles/m³ | Recommended Limits for Microbial Contamination | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At Rest | In Operation | Air Sample | Settle Plates (Diameter 90 mm) |
Contact Plates (Diameter 55 mm) |
Glove Print 5 Fingers |
|||
| 0.5 µm | 5 µm | 0.5 µm | 5 µm | cfu/m³ | cfu/4hr | cfu/deska | cfu/glove | |
| A | 3,520 | 20 | 3,520 | 20 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| B | 3,520 | 29 | 352,000 | 2,900 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| C | 352,000 | 2,900 | 3,520,000 | 29,000 | 100 | 50 | 25 | -- |
| D | 3,520,000 | 29,000 | * | * | 200 | 100 | 50 | -- |
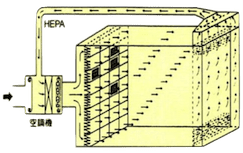
Air Flow Design
Based on different clean room levels, different airflow is designed. It is popularly divided as follows: vertical laminar flow (class 1~100), horizontal laminar flow (class 1~1,000), turbulent flow (class 1,000~100,000). This difference is namely as here below table.
| Vertical Laminar Flow | Horizontal Laminar Flow | Turbulent Flow | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Flow Chart | 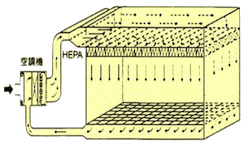 |
 |
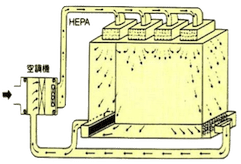 |
| Air Flow Direction | Clean air flows from the ceiling to the floor. | Clean air flows from one wall to the opposite wall. | Clean air flows in an unidirectional way. |
| Outlet Vent | Blow out: 80%-100% on ceiling area. | Blow out: over 80% on wall. | Blow out: outlet of filter is better. |
| Intake Vent | Suck in: over 40% on floor area. | Suck in: over 40% on wall, also promote on ceiling. | Suck in: on neighboring floor area. |
| Clean Level | Used in class 1 - 100 | Used in class 1 - 10,000 | Used in class 1,000 - 100,000 |
| Air Change Rate | 300 - 600 times/hr | C-100: 250 - 350 times/hr C-1K: 60 - 120 times/hr |
C-1K: 60 - 120 times/hr C-10K: 35 - 45 times/hr |
| PRO |
|
|
|
| CON |
|
|
|
Testing and Certification
The purpose of testing or validating an air-conditioning system is to ensure that the system continuously and steadily controls the air quality at the workplace, so that products can be manufactured at a high quality and free from contamination.
Testing Timing
There are three timing for testing a cleanroom, which are as-built, as-rest, and operational.
- As-Built
The empty room. - As-Rest
The room fitted with machinery but no personnel present. - Operational
The room fitted with machinery and persons in operation.
Testing and Validation Items
Not every testing needs to be preformed at these three testing timing as above. It depends on its type and requirements in design.
- Wind speed and air volume testing
- Air laminarity testing
- Particle counting
- Microbes counting
- Temperature and humidity readings
- Differential pressure measurements
- Filter leak testing
- Room integrity testing
- Recovery performance testing
- Light and noise level readings
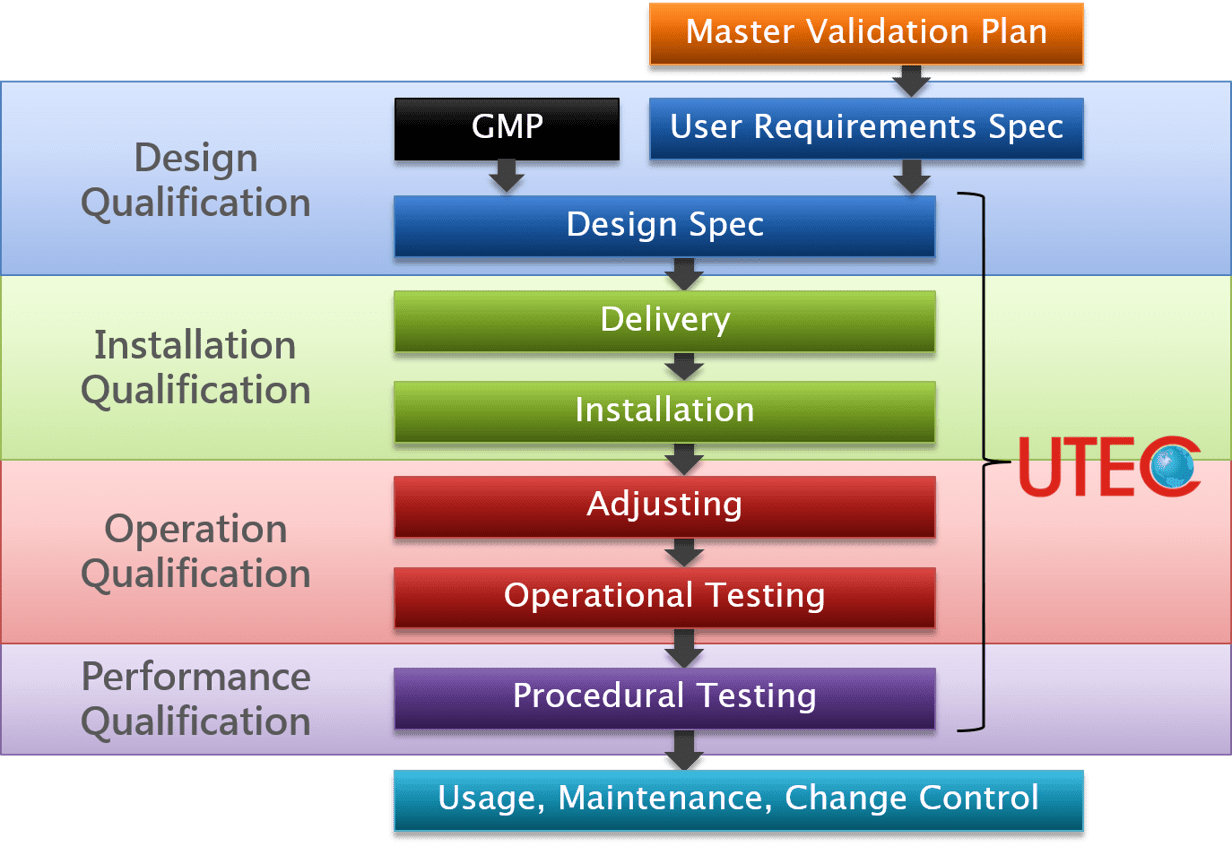
Validation Plan and Process
For industries involved in pharmaceutical and health care products, or even laboratories, product quality is paramount and minute inconsistencies can have disastrous results. Design Qualification (DQ), Installation Qualification (IQ), Operational Qualification (OQ) and Performance Qualification (PQ) are essential parts of quality assurance of a HVAC system validation.